Ansible Automation Platform Operator
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform’s latest release supports Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions 8 and 9 and Red Hat Openshift (the Red Hat Enterprise release of Kubernetes). The Ansible Automation Platform Operator provides cloud-native, easy-to-install deployment of Ansible Automation Platform instances in our OpenShift environment version 4.9+.
AAP Operator installation
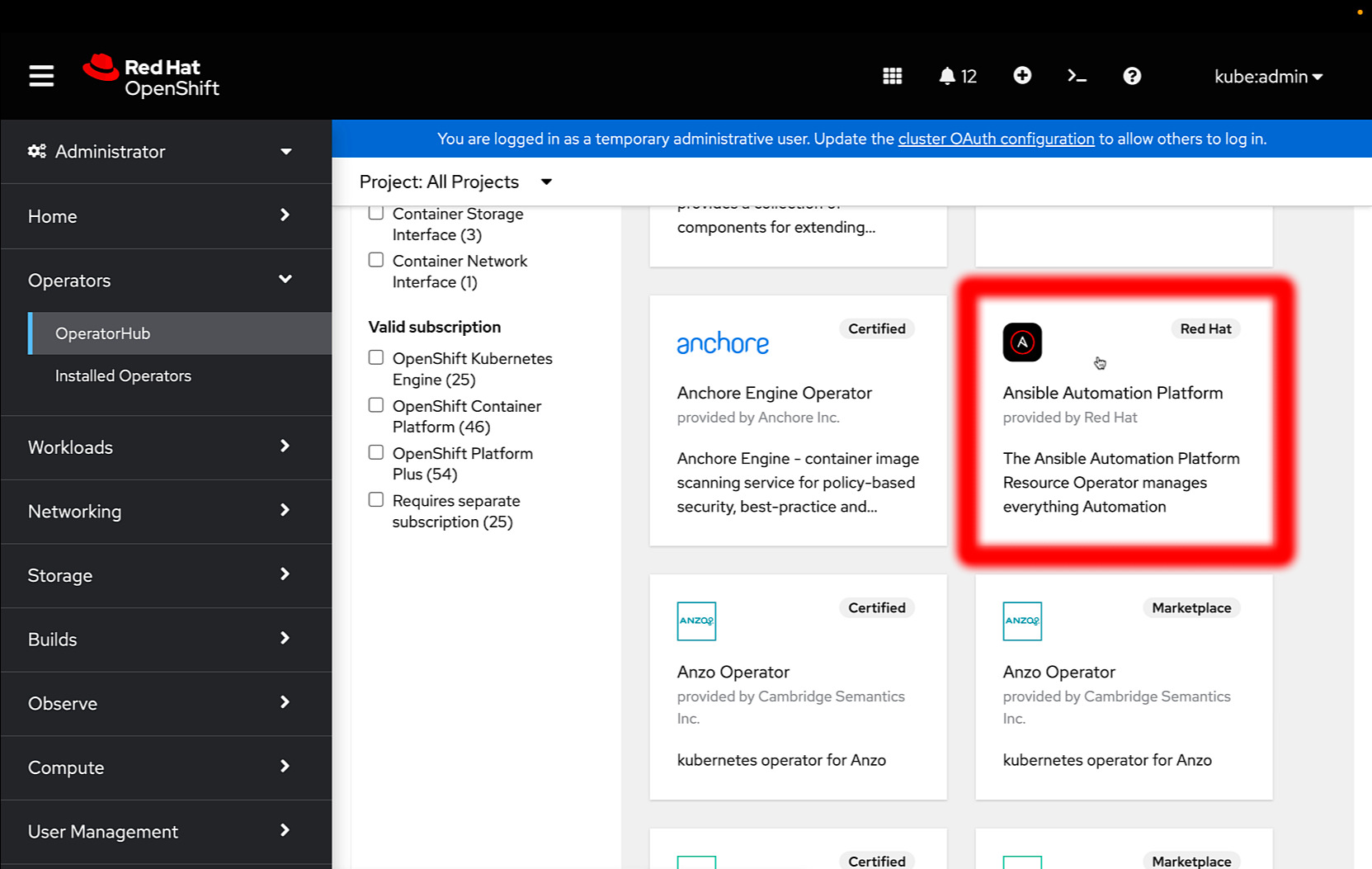
The easiest way is to install the Ansible Automation Platform Operator via the OperatorHub in the web console. Search for “Ansible Automation Platform”, latest release is 2.3.0+0.1674778407. The operator installs all the dependencies, such as PostgreSQL 13.
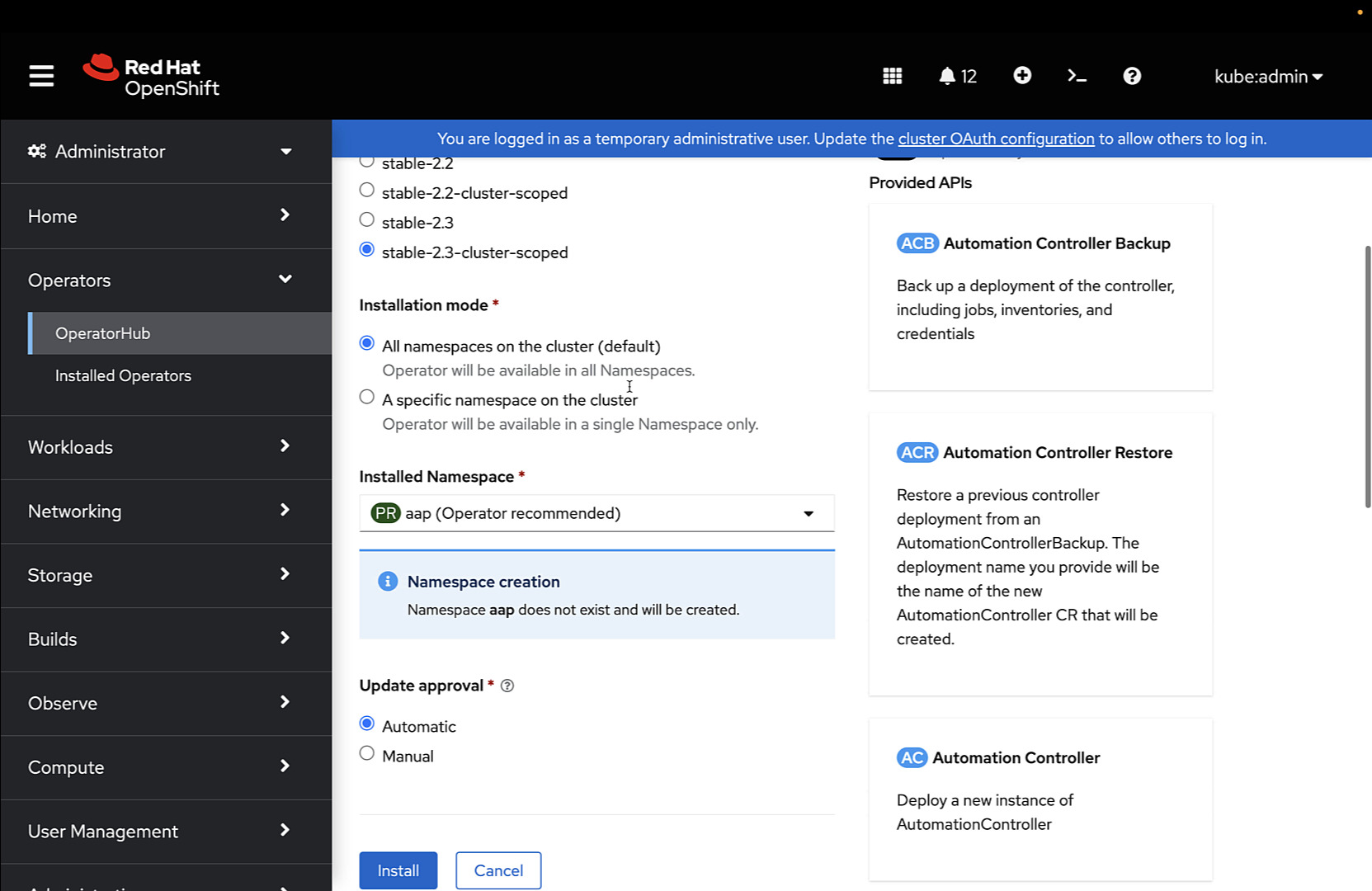
Some parameters of the Ansible Automation Platform Operator installation:
- Update Channel: the exact version to install
- Installation mode: install the operator cluster-wise or only in a specific namespace
- Installed namespace: customize the default is the “aap” namespace
- Update approval: manual or automatic
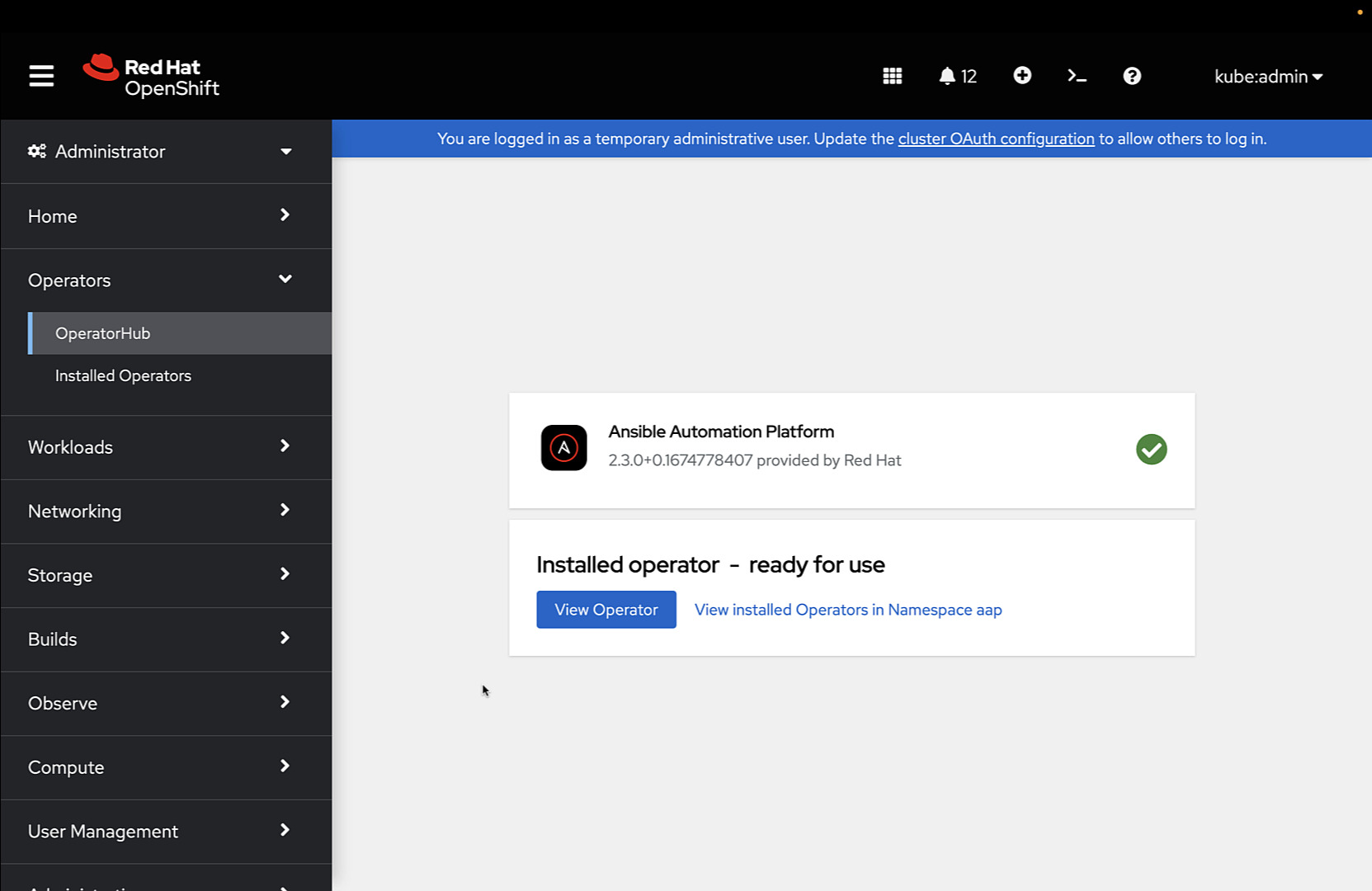
AAP Operator usage
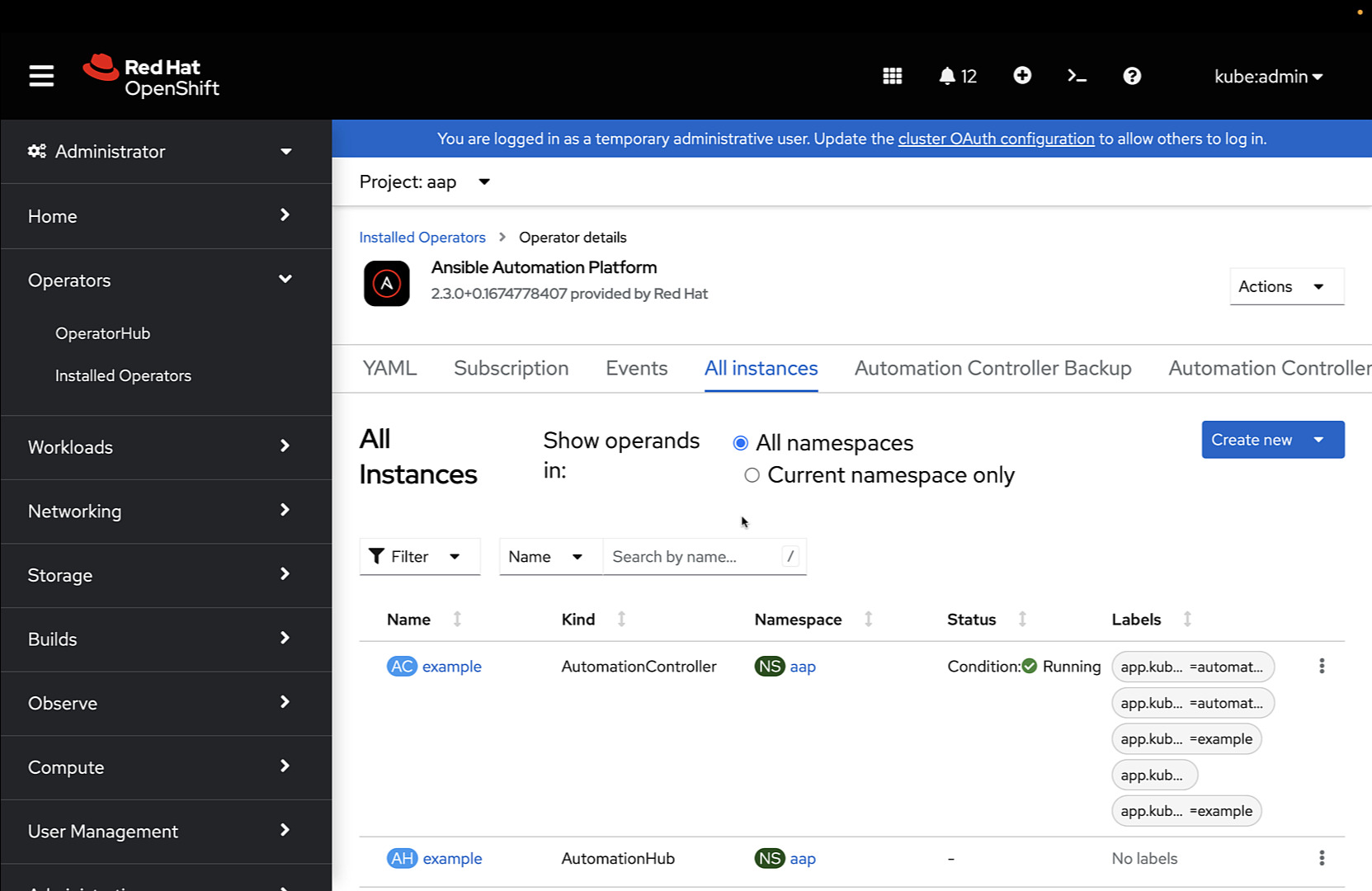
Once successfully installed, can access the Operator Dashboard to create instances of:
- Automation Controller (AC): Deploy a new instance of AutomationController
- Automation Controller Backup (ACB): Back up deployment of the controller, including jobs, inventories, and credentials
- Automation Controller Restore (ACR): Restore a previous controller deployment from an AutomationControllerBackup. The deployment name you provide will be the name of the new AutomationController CR that will be created.
- Automation Controller job template (JT): Define a new job template in the controller
- Automation Controller job (AJ): Launch a new job via controller
- Automation Hub (AH): Deploy a new instance of Automation Hub
- Automation Hub Backup (AHB): Back up deployment of the hub, including all hosted Ansible content, secrets, and the database. By default, a persistent volume claim will be created using the default StorageClass on your cluster to store the backup.
- Automation Hub Restore (AHR): Restore a previous hub deployment into the namespace.
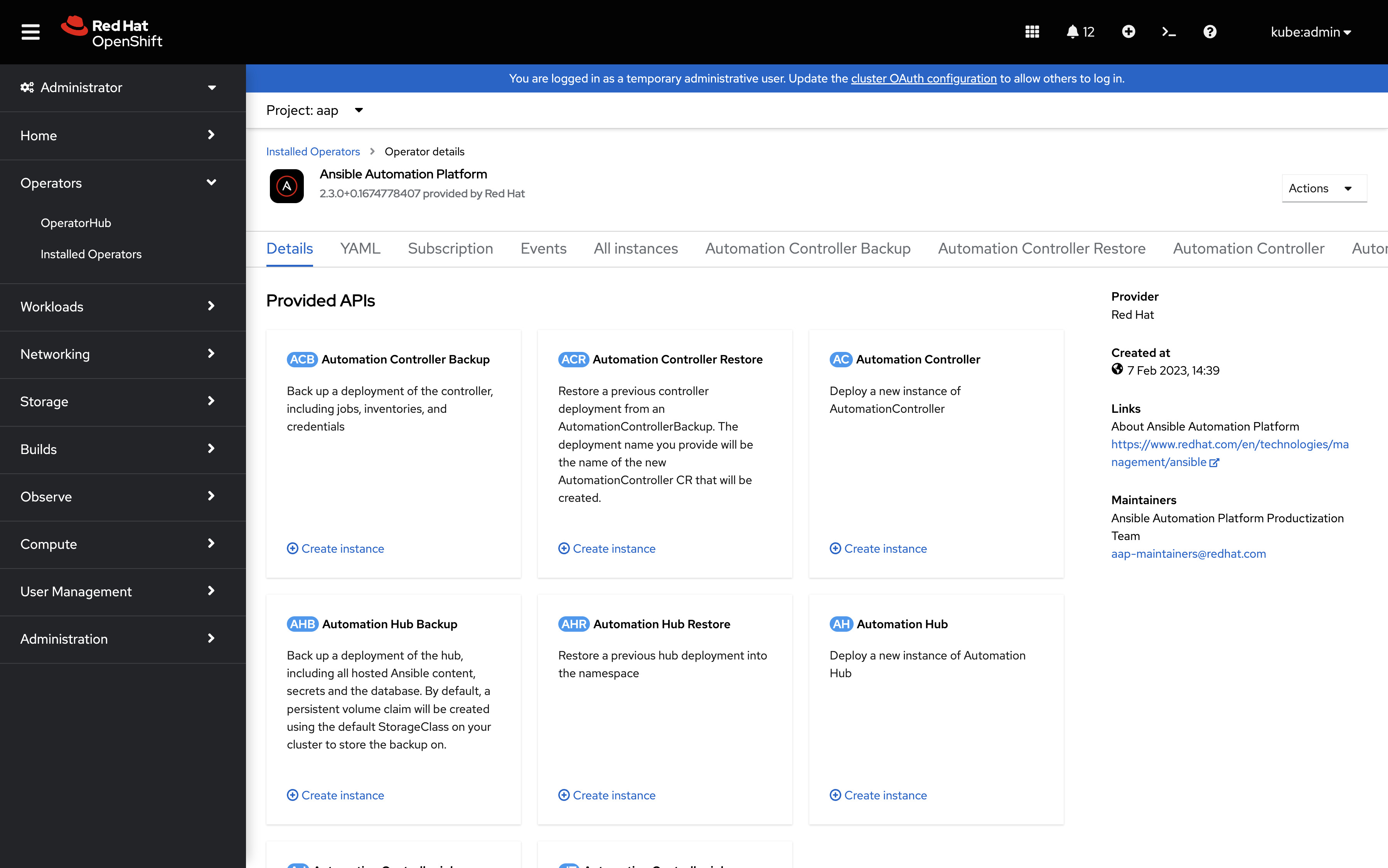
We can create an instance of the Ansible Controller and access the Web dashboard to create users applying RBAC access criteria, fetch Ansible projects from the most common SCM, and run our automation using the Job Templates. The Ansible Controller Dashboard:
Conclusion
Installing the Ansible Automation Platform in Red Hat OpenShift (OCP) is easy using the AAP Operator. It simplifies the lifecycle of the Ansible Controller and Automation Hub instances.
Subscribe to the YouTube channel, Medium, and Website, X (formerly Twitter) to not miss the next episode of the Ansible Pilot.Academy
Learn the Ansible automation technology with some real-life examples in my
Udemy 300+ Lessons Video Course.

My book Ansible By Examples: 200+ Automation Examples For Linux and Windows System Administrator and DevOps

Donate
Want to keep this project going? Please donate