Introduction
In the world of automation and configuration management, Ansible plays a pivotal role in simplifying complex tasks and orchestrating diverse systems. One of the key features that makes Ansible highly versatile is the ability to extend its functionality through plugins. In this article, we’ll dive into the “hello-world" filter plugin written in Python for Ansible within the foo.bar namespace.
Understanding the Basics
The “hello-world” filter plugin is a simple yet illustrative example of a filter plugin in Ansible. The purpose of this plugin is to generate a personalized greeting message, taking a name as input and returning a “Hello, [name]” message.
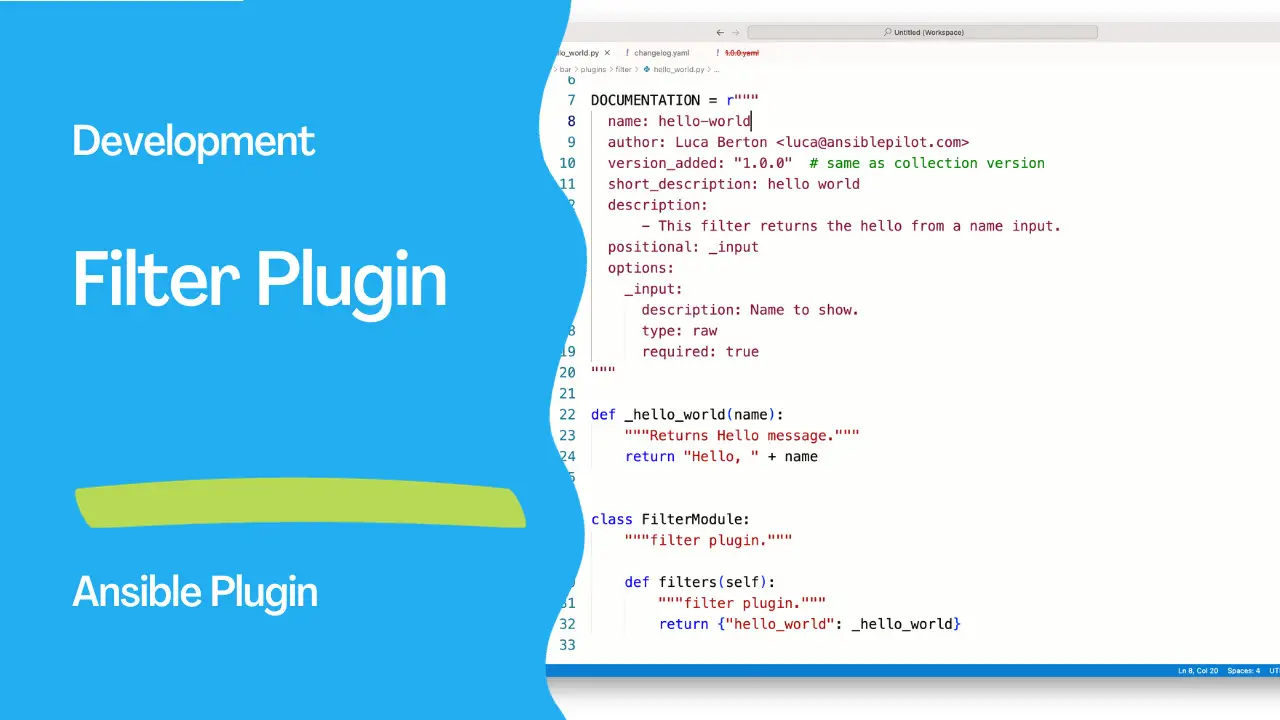
"""A hello-world filter plugin in foo.bar collection."""
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function
__metaclass__ = type
DOCUMENTATION = r"""
name: hello-world
author: Luca Berton <[email protected]>
version_added: "1.0.0" # same as collection version
short_description: hello world
description:
- This filter returns the hello from a name input.
positional: _input
options:
_input:
description: Name to show.
type: raw
required: true
"""
def _hello_world(name):
"""Returns Hello message."""
return "Hello, " + name
class FilterModule:
"""filter plugin."""
def filters(self):
"""filter plugin."""
return {"hello_world": _hello_world}

Let’s break down the key components of the provided Python script, hello_world.py:
- Metadata Section:
name: Specifies the name of the filter plugin.author: Indicates the author of the plugin along with their contact email.version_added: Denotes the version in which the plugin was added.short_description: Provides a brief overview of the plugin.description: Offers more detailed information about the plugin, including its purpose.positional: Defines the positional arguments that the plugin accepts.options: Describes the options, such as input parameters, that the plugin supports.
- Filter Implementation:
_hello_worldfunction: This private function takes a name as an argument and returns a greeting message.FilterModuleclass: Defines the filter plugin and its associated methods. filters method: Specifies the filters provided by the plugin. In this case, it includes the “hello_world” filter, which is mapped to the_hello_worldfunction.
Practical Use
To utilize this filter plugin in an Ansible playbook, you can invoke it using the hello_world filter with a specific name as input. Here’s an example:
---
- name: Example Playbook
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: Display Hello World Message
debug:
msg: "{{ 'Your Name' | hello_world }}"
Replace ‘Your Name’ with the desired name, and when you run this playbook, it will output a message like:
TASK [Display Hello World Message] ********************************************
ok: [localhost] => {
"msg": "Hello, Your Name"
}
Conclusion
Understanding filter plugins in Ansible is crucial for extending the capabilities of your automation scripts. The “hello-world” filter plugin we explored provides a foundation for creating more complex filters tailored to specific use cases. By customizing and expanding upon this example, you can enhance your Ansible playbooks with personalized and dynamic content. Happy automating!
Academy
Learn the Ansible automation technology with some real-life examples in my
Udemy 300+ Lessons Video Course.

My book Ansible By Examples: 200+ Automation Examples For Linux and Windows System Administrator and DevOps

Donate
Want to keep this project going? Please donate