How to create Kubernetes K8s or OpenShift OCP Service with Ansible?
I’m going to show you a live Playbook and some simple Ansible code. I’m Luca Berton and welcome to today’s episode of Ansible Pilot.
Ansible create Kubernetes or OpenShift Service
kubernetes.core.k8s- Manage Kubernetes (K8s) objects
Let’s talk about the Ansible module k8s.
The full name is kubernetes.core.k8s, which means that is part of the collection of modules of Ansible to interact with Kubernetes and Red Hat OpenShift clusters.
It manages Kubernetes (K8s) objects.
Parameters
- name string /namespace string - object name / namespace
- api_version string - “v1”
- kind string - object model
- state string - present/absent/patched
- definition string - YAML definition
- src path - path for YAML definition
- template raw - YAML template definition
- validate dictionary - validate resource definition
There is a long list of parameters of the k8s module. Let me summarize the most used.
Most of the parameters are very generic and allow you to combine them for many use-cases.
The name and namespace specify object name and/or the object namespace. They are useful to create, delete, or discover an object without providing a full resource definition.
The api_version parameter specifies the Kubernetes API version, the default is “v1” for version 1.
The kind parameter specifies an object model.
The state like for other modules determines if an object should be created - present option, patched - patched option, or deleted - absent option.
The definition parameter allows you to provide a valid YAML definition (string, list, or dict) for an object when creating or updating.
If you prefer to specify a file for the YAML definition, the src parameter provides a path to a file containing a valid YAML definition of an object or objects to be created or updated.
You could also specify a YAML definition template with the template parameter.
You might find useful also the validate parameter in order to define how to validate the resource definition against the Kubernetes schema. Please note that requires the kubernetes-validate python module.
Links

Playbook
How to create Kubernetes Service with Ansible Playbook using the module k8s.
Specifically, the following example is going to create the “nginx-service” Service and “nginx” Pod in namespace “example” of Kubernetes K8s or OpenShift OCP with Ansible.
code
- ansible_playbook.yml
---
- name: k8s Playbook
hosts: localhost
gather_facts: false
connection: local
vars:
myproject: "example"
tasks:
- name: create k8s service
kubernetes.core.k8s:
src: myservice.yaml
namespace: "{{ myproject }}"
state: present
- myservice.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: proxy
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.21.6
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: http-web-svc
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: proxy
ports:
- name: service-port
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: http-web-svc
execution
ansible-pilot $ ansible-playbook kubernetes/service.yml
[WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that the implicit
localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [k8s Playbook] ***********************************************************************************
TASK [create k8s service] *************************************************************************
changed: [localhost]
PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************
localhost : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
ansible-pilot $
idempotency
ansible-pilot $ ansible-playbook kubernetes/service.yml
[WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that the implicit
localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [k8s Playbook] ***********************************************************************************
TASK [create k8s service] *************************************************************************
ok: [localhost]
PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************
localhost : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
ansible-pilot $
before execution
- Kubernetes (k8s)
ansible-pilot $ kubectl project example
Already on project "example" on server "https://api.crc.testing:6443".
ansible-pilot $ kubectl get svc
No resources found in example namespace.
ansible-pilot $ kubectl get pods
No resources found in example namespace.
ansible-pilot $
- OpenShift (OCP)
ansible-pilot $ oc project example
Already on project "example" on server "https://api.crc.testing:6443".
ansible-pilot $ oc get svc
No resources found in example namespace.
ansible-pilot $ oc get pods
No resources found in example namespace.
ansible-pilot $
after execution
- Kubernetes (k8s)
ansible-pilot $ kubectl project example
Already on project "example" on server "https://api.crc.testing:6443".
ansible-pilot $ kubectl get svc
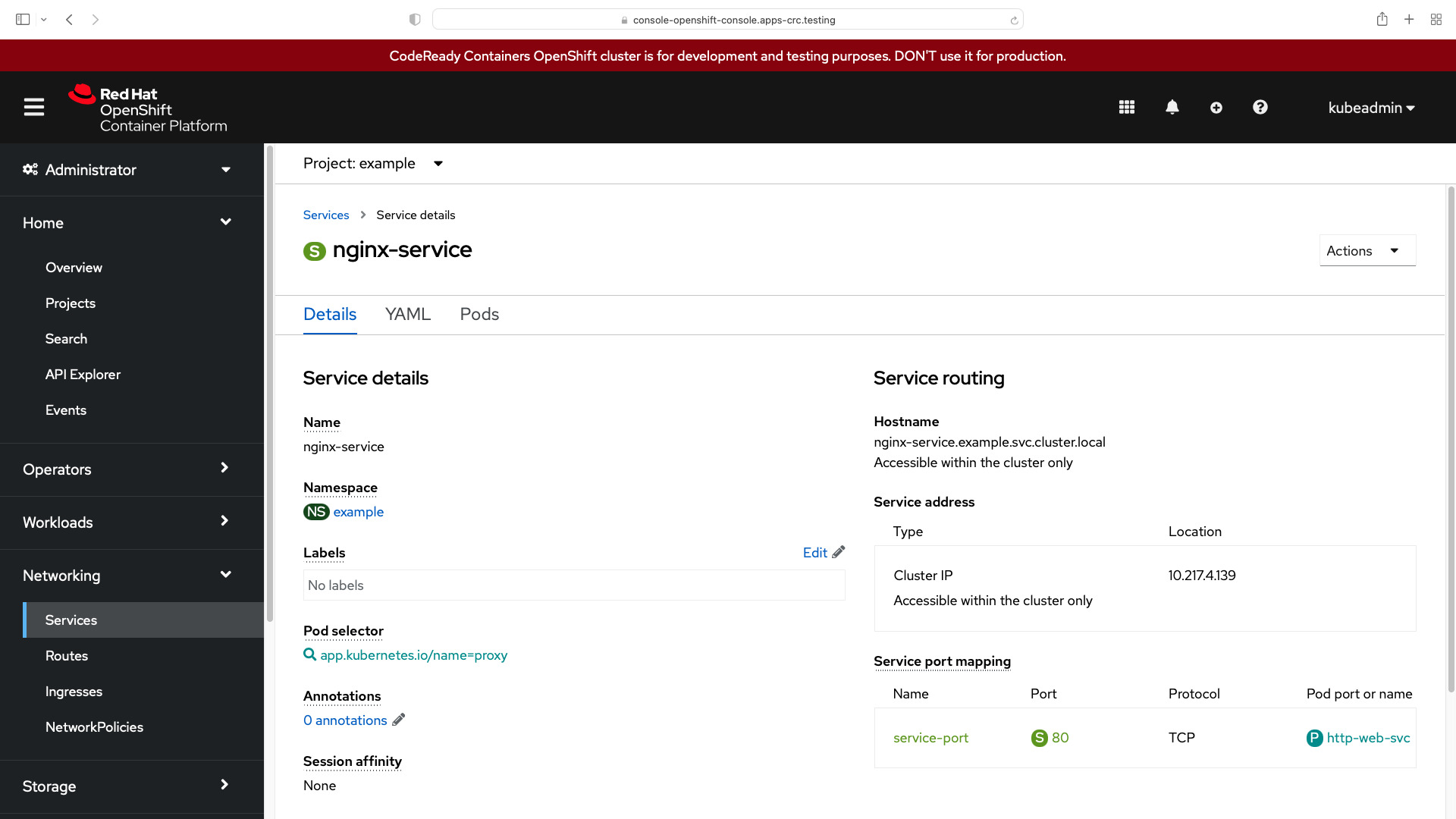
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-service ClusterIP 10.217.4.139 <none> 80/TCP 23s
ansible-pilot $ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx 1/1 Running 0 34s
ansible-pilot $
- OpenShift (OCP)
ansible-pilot $ oc project example
Already on project "example" on server "https://api.crc.testing:6443".
ansible-pilot $ oc get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx-service ClusterIP 10.217.4.139 <none> 80/TCP 23s
ansible-pilot $ oc get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx 1/1 Running 0 34s
ansible-pilot $
- Kubernets nginx-service YAML
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: nginx-service
namespace: example
uid: 7069d677-6fd2-430c-82c6-3b1d596b722b
resourceVersion: '205491'
creationTimestamp: '2022-04-13T08:58:53Z'
managedFields:
- manager: OpenAPI-Generator
operation: Update
apiVersion: v1
time: '2022-04-13T08:58:53Z'
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
'f:spec':
'f:internalTrafficPolicy': {}
'f:ports':
.: {}
'k:{"port":80,"protocol":"TCP"}':
.: {}
'f:name': {}
'f:port': {}
'f:protocol': {}
'f:targetPort': {}
'f:selector': {}
'f:sessionAffinity': {}
'f:type': {}
spec:
clusterIP: 10.217.5.138
ipFamilies:
- IPv4
ports:
- name: service-port
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: http-web-svc
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
clusterIPs:
- 10.217.5.138
type: ClusterIP
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
sessionAffinity: None
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: proxy
status:
loadBalancer: {}
Conclusion
Now you know how to create Kubernetes or OpenShift Service with Ansible.
Subscribe to the YouTube channel, Medium, and Website, X (formerly Twitter) to not miss the next episode of the Ansible Pilot.Academy
Learn the Ansible automation technology with some real-life examples in my
Udemy 300+ Lessons Video Course.

My book Ansible By Examples: 200+ Automation Examples For Linux and Windows System Administrator and DevOps

Donate
Want to keep this project going? Please donate
