How to configure a Windows Host for Ansible?
I’ll show you step by step on a freshly installed machine how to configure a “basic” authentication, use a Local Accounts for authentication and successfully execute a simple “win_ping” Ansible Playbook. This initial configuration sometimes is a roadblock for some Windows users to start using Ansible. I’m Luca Berton and welcome to today’s episode of Ansible Pilot.
Configure a Windows Host for Ansible
- Windows 7, 8.1, 10, 11
- Windows Server 2008, 2008 R2, 2012, 2012 R2, 2016, 2019, 2022
- PowerShell 3.0+ and .NET 4.0+
- WinRM or OpenSSH (experimental)
The supported nodes include all the modern releases of Windows Desktop and Server. The full list includes Windows 7, 8.1, 10, 11, and Windows Server 2008, 2008 R2, 2012, 2012 R2, 2016, 2019, 2022. Ansible requires PowerShell 3.0 or newer and at least .NET 4.0 to be installed on the Windows host. You need to upgrade only old Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 nodes. The communication between Ansible Controller and the target node is executed via a WinRM listener that needs to be created and activated. Ansible 2.8 has added an experimental SSH connection for Windows-managed nodes for Windows 10+ clients and Windows Server 2019+. In this example, we’re going to cover the WinRM connection method with “basic” authentication. Refer to manual for more WinRM wide range of configuration options.
Links

Playbook
How to configure a Windows Host for Ansible connections.
- Create a user
- verify PowerShell & .NET
- setup WinRM
- create Inventory & Playbook
First of all, I’d suggest creating a user to run Ansible automation. This user needs to be Power User or have Administrative privileges in order to execute some Ansible code.
Second, you need to verify that PowerShell and .NET versions, modern operating systems already meet the requirements.
The most important part is to set up the WinRM. There is a great PowerShell script that sets up both HTTP and HTTPS listeners with a self-signed certificate and enables the Basic authentication option on the service.
Once everything is done on the node you could configure the Ansible inventory on the Ansible Controller machine and run your first Ansible Playbook with the win_ping module to verify the successful configuration.
Windows node
Create an “ansible” user
- open Computer Management (right-click from “This PC” > “Manage”)
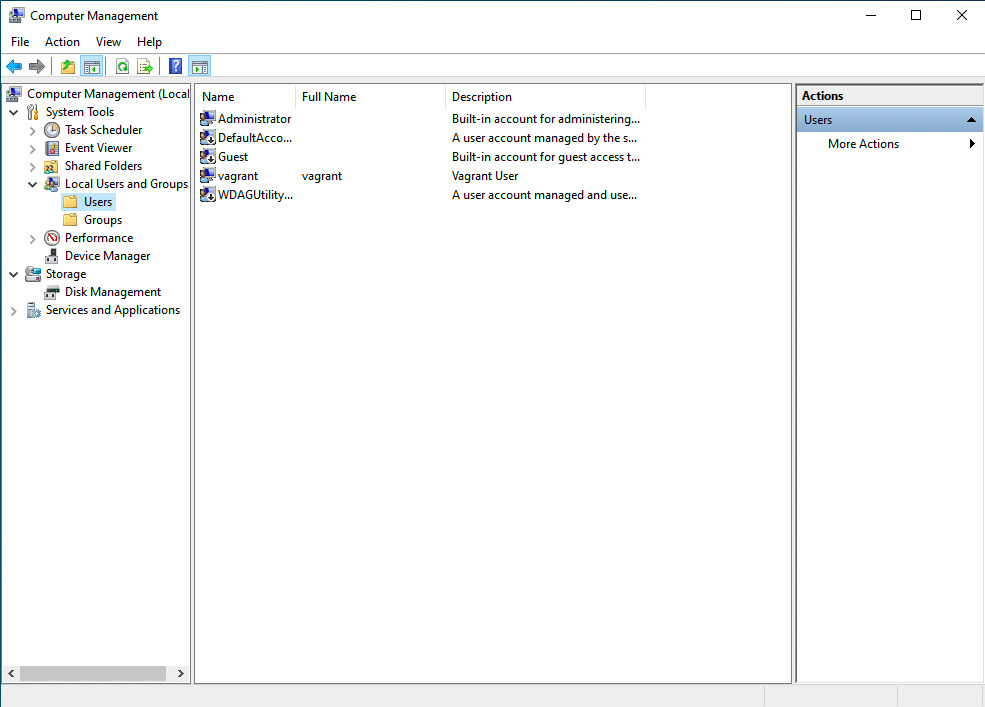
- New User (right-click from “Users” > “New User”)
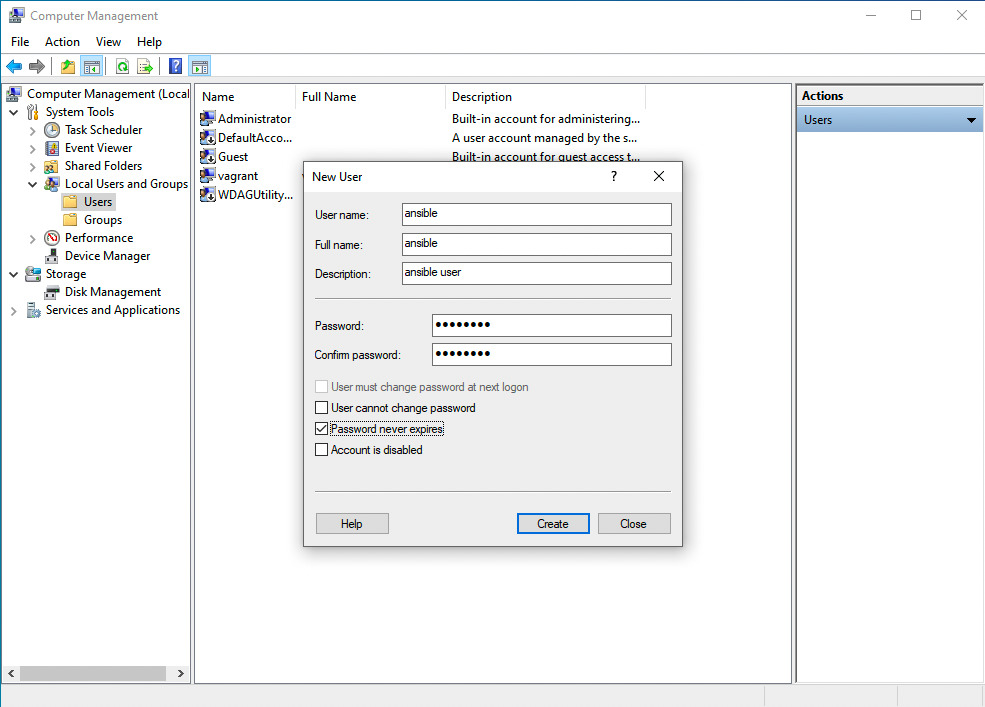
User name: ansible
Full name: ansible
Description: ansible user
Password and Confirm password: SuperSecurePassword123@
Options: enable Password never expires disable User must change password at next logon
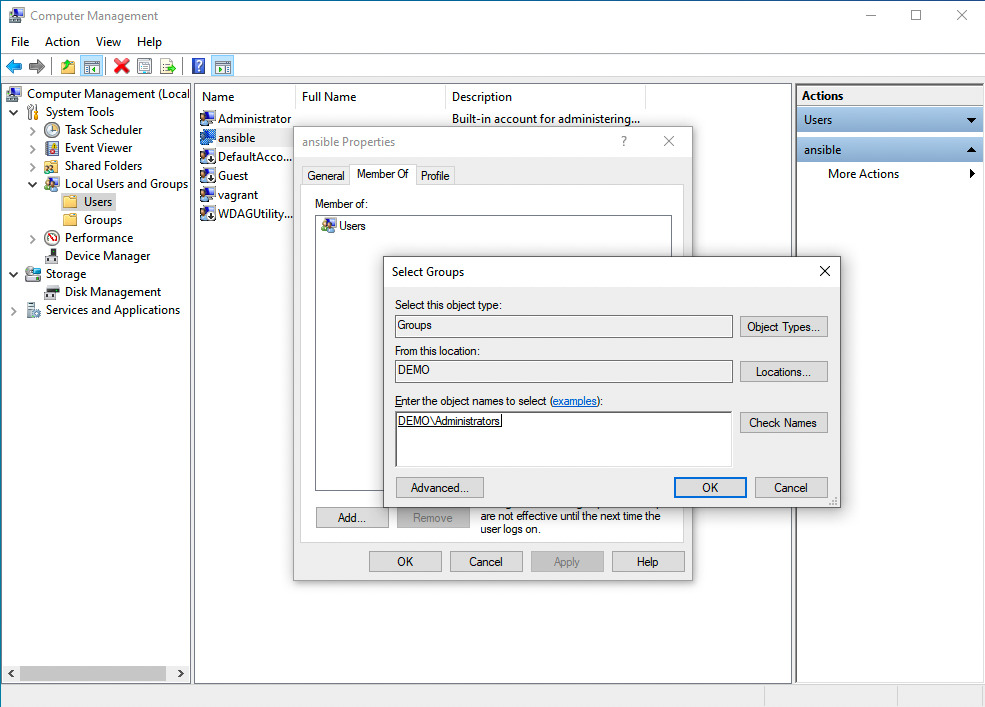
- Add “ansible” user to “administrators” Group
Verify PowerShell, .NET and set up WinRM
- verify PowerShell version
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Try the new cross-platform PowerShell https://aka.ms/pscore6
PS C:\Users\vagrant> Get-Host | Select-Object Version
Version
-------
5.1.19041.1237
- verify .NET version
PS C:\Users\vagrant> Get-ChildItem 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP' -Recurse | Get-ItemProperty -Name version -EA 0 | Where { $_.PSChildName -Match '^(?!S)\p{L}'} | Select PSChildName, version
>>
PSChildName Version
----------- -------
Client 4.8.04084
Full 4.8.04084
Client 4.0.0.0
PS C:\Users\vagrant>
- Verify WinRM not-configured
PS C:\Users\vagrant> winrm get winrm/config/Service
WSManFault
Message = The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig".
Error number: -2144108526 0x80338012
The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig".
PS C:\Users\vagrant> winrm get winrm/config/Winrs
WSManFault
Message = The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig".
Error number: -2144108526 0x80338012
The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig".
PS C:\Users\vagrant> winrm enumerate winrm/config/Listener
WSManFault
Message = The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig".
Error number: -2144108526 0x80338012
The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig".
PS C:\Users\vagrant>
- Setup WinRM
PS C:\Users\vagrant> [Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
>> $url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ansible/ansible/devel/examples/scripts/ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1"
>> $file = "$env:temp\ConfigureRemotingForAnsible.ps1"
>>
>> (New-Object -TypeName System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile($url, $file)
>>
>> powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -File $file
PS C:\Users\vagrant>
- Verify WinRM configured
PS C:\Users\vagrant> winrm get winrm/config/Service
Service
RootSDDL = O:NSG:BAD:P(A;;GA;;;BA)(A;;GR;;;IU)S:P(AU;FA;GA;;;WD)(AU;SA;GXGW;;;WD)
MaxConcurrentOperations = 4294967295
MaxConcurrentOperationsPerUser = 1500
EnumerationTimeoutms = 240000
MaxConnections = 300
MaxPacketRetrievalTimeSeconds = 120
AllowUnencrypted = true
Auth
Basic = true
Kerberos = true
Negotiate = true
Certificate = false
CredSSP = false
CbtHardeningLevel = Relaxed
DefaultPorts
HTTP = 5985
HTTPS = 5986
IPv4Filter = *
IPv6Filter = *
EnableCompatibilityHttpListener = false
EnableCompatibilityHttpsListener = false
CertificateThumbprint
AllowRemoteAccess = true
PS C:\Users\vagrant>
PS C:\Users\vagrant> winrm get winrm/config/Winrs
Winrs
AllowRemoteShellAccess = true
IdleTimeout = 7200000
MaxConcurrentUsers = 2147483647
MaxShellRunTime = 2147483647
MaxProcessesPerShell = 2147483647
MaxMemoryPerShellMB = 2147483647
MaxShellsPerUser = 2147483647
PS C:\Users\vagrant> winrm enumerate winrm/config/Listener
Listener
Address = *
Transport = HTTPS
Port = 5986
Hostname = WIN10
Enabled = true
URLPrefix = wsman
CertificateThumbprint = F4D065F8FC6EE18F1F0FF9533584955D0C9B8E59
ListeningOn = 10.0.2.15, 127.0.0.1, 169.254.20.54, ::1, fe80::44a1:482d:5918:7cb4%4, fe80::d017:a935:ff50:4eb4%5
PS C:\Users\vagrant> winrm enumerate winrm/config/Listener
Listener
Address = *
Transport = HTTPS
Port = 5986
Hostname = WIN10
Enabled = true
URLPrefix = wsman
CertificateThumbprint = F4D065F8FC6EE18F1F0FF9533584955D0C9B8E59
ListeningOn = 10.0.2.15, 127.0.0.1, 192.168.0.83, ::1, fe80::94b1:dc79:39cf:8b61%4, fe80::d017:a935:ff50:4eb4%5
PS C:\Users\vagrant>
Ansible Controller
code
- inventory
[windows]
windows10 ansible_host=192.168.0.59
[windows:vars]
ansible_user=ansible
ansible_password=SuperSecurePassword123@
ansible_port=5986
ansible_connection=winrm
ansible_winrm_transport=basic
ansible_winrm_server_cert_validation=ignore
- win_ping.yml
---
- name: win_ping module Playbook
hosts: windows
become: false
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: test connection
ansible.windows.win_ping:
execution
ansible-pilot $ ansible-playbook -i windows/inventory windows/win_ping.yml
PLAY [win_ping module Playbook] ***********************************************************************
TASK [test connection] ****************************************************************************
ok: [windows10]
PLAY RECAP ****************************************************************************************
windows10 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
ansible-pilot $
Conclusion
Now you know Configure a Windows Host for Ansible. Subscribe to the YouTube channel, Medium, and Website, X (formerly Twitter) to not miss the next episode of the Ansible Pilot.
Academy
Learn the Ansible automation technology with some real-life examples in my
Udemy 300+ Lessons Video Course.

My book Ansible By Examples: 200+ Automation Examples For Linux and Windows System Administrator and DevOps

Donate
Want to keep this project going? Please donate
